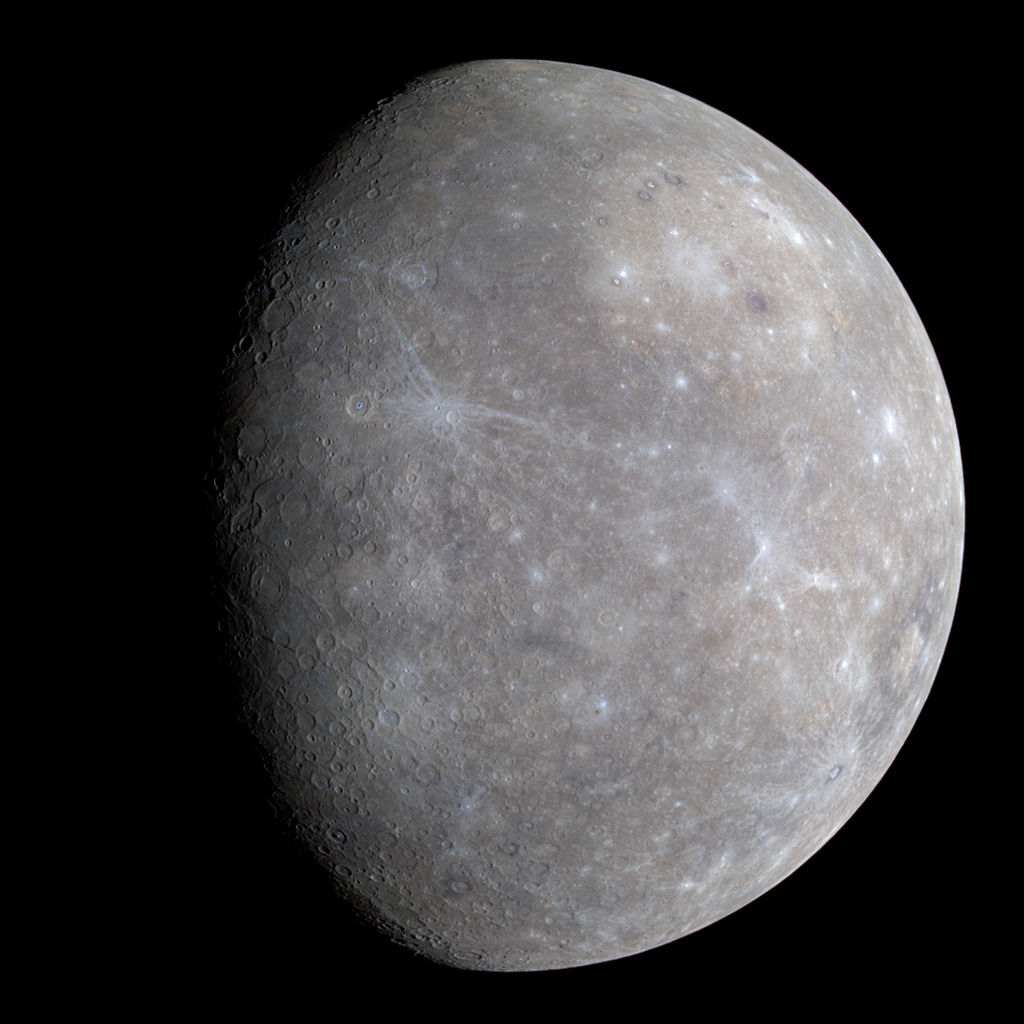
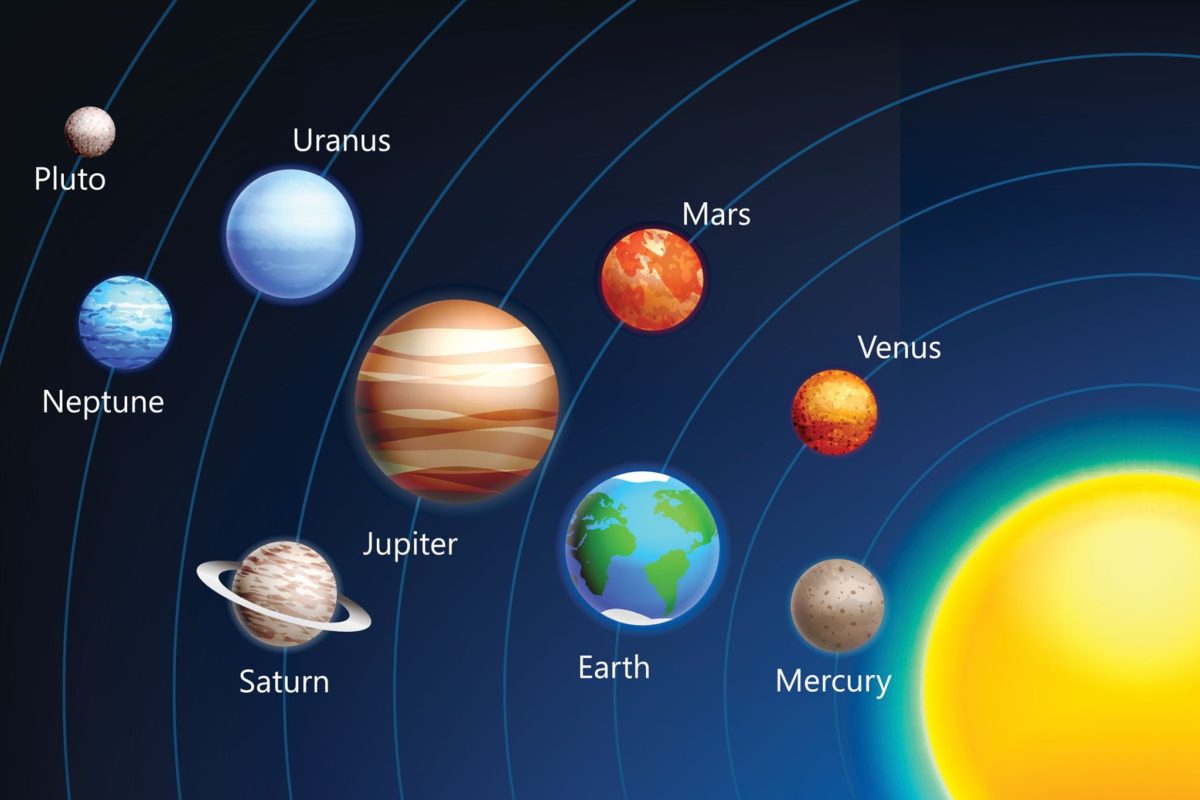
Izraz planet je starodaven in je povezan z zgodovino, astrologijo, znanostjo, mitologijo in religijo. Poleg same Zemlje je s prostim očesom pogosto vidnih tudi pet planetov v Osončju. Mnoge zgodnje kulture so jih imele za božanske ali kot odposlance božanstev. Z napredovanjem znanstvenih spoznanj se je človeško dojemanje planetov spremenilo in vključilo številne različne predmete. Leta 2006 je Mednarodna astronomska zveza (IAU) uradno sprejela resolucijo, ki opredeljuje planete v Osončju. Ta opredelitev je sporna, ker izključuje številne predmete planetarne mase glede na to, kje ali kaj krožijo. Čeprav osem planetarnih teles, odkritih pred letom 1950, po sedanji definiciji ostajajo “planeti”, nekatera nebesna telesa, kot so Ceres, Pallas, Junona in Vesta (vsaka je objekt v pasu sončnih asteroidov) in Pluton (prva transneptunska predmet odkrit), ki jih je znanstvena skupnost nekoč štela za planete, po sedanji definiciji planeta niso več videti kot planeti.
Planeti 2